top of page
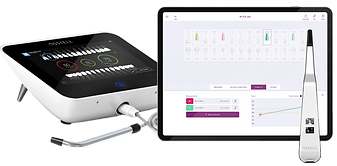
Ensuring implant stability
Resonance Frequency Analysis (RFA) is a sophisticated technique used in dentistry to assess the stability and osseointegration of dental implants. This method involves the use of specialized instruments, such as Osstell, which utilize a small transducer attached to the implant. The transducer emits a mechanical impulse or vibration, causing the implant to vibrate at its natural frequency. By measuring the frequency of these vibrations, RFA provides quantitative data on the stability of the implant-bone interface.
The principle behind RFA is based on the fact that the stiffness of the implant-bone interface changes as osseointegration progresses. In the early stages of healing, the implant is less rigidly attached to the surrounding bone, resulting in lower resonance frequencies. As osseointegration occurs and the bone fuses with the implant surface, the stiffness of the interface increases, leading to higher resonance frequencies. By analyzing these frequency measurements, clinicians can assess the degree of osseointegration and determine the optimal timing for loading the implant with a restoration. RFA offers a non-invasive and objective method for evaluating implant stability, allowing for more informed treatment decisions and improved long-term outcomes for patients undergoing dental implant therapy.
bottom of page
